Access to clean and reliable water is a fundamental need—yet in many parts of the world, traditional pumping systems fall short due to rising energy costs, limited grid access, or environmental concerns. This is where solar pump inverters are changing the game. These innovative devices convert solar energy into usable power for water pumps, providing a sustainable and cost-effective solution for agriculture, livestock, rural supply, and environmental management.
In this guide, we’ll explore what a solar pump inverter is, how it works, the components involved, and the many ways it’s being used across diverse industries. Whether you’re new to solar technology or looking to upgrade an existing system, understanding the role of solar pump inverters can help you build more resilient, energy-efficient water infrastructure.
What Is a Solar Pump Inverter?
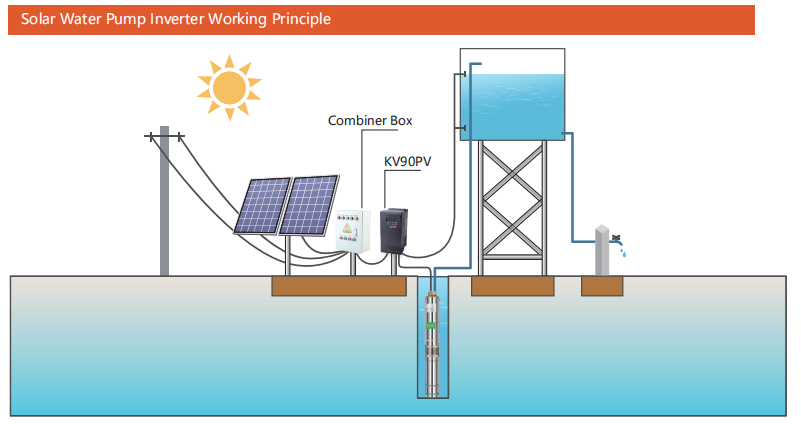
A solar pump inverter is a key component in solar-powered water pumping systems, especially in regions where grid electricity is unreliable or unavailable. It converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar photovoltaic (PV) panels into alternating current (AC), which is required to run traditional electric water pumps. This allows solar energy to directly power the irrigation and water supply infrastructure in off-grid or semi-grid environments.
But a solar pump inverter is more than just a power converter—it’s also a smart controller. It monitors the energy input from the solar panels and adjusts the output to match the operational needs of the pump, ensuring optimal performance even as sunlight intensity changes throughout the day. In this way, the inverter acts as both the brain and heart of the solar water pumping system.
Modern solar pump inverters—especially those designed with Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) technology—maximize energy harvesting by continuously optimizing the voltage and current from solar panels. This not only improves the system’s energy efficiency but also reduces the number of solar panels required, thereby lowering total system costs.
Solar pump inverters are widely used in agricultural irrigation, livestock watering, village water supply, and water treatment applications. With growing concerns over fossil fuel costs and carbon emissions, these devices offer a clean, affordable, and scalable alternative for water access across the globe.

What Are the Core Components of a Solar Pump System?
A well-designed solar pump system is composed of several essential components working seamlessly together. Each plays a critical role in capturing, converting, and delivering solar energy to power water pumps effectively. Below is a breakdown of the core elements that make up a reliable solar water-pumping solution.
1. Solar Panels: The Energy Source
Solar panels are the starting point of the system. They absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. Panels are usually positioned at optimal angles to maximize sunlight exposure throughout the day. Depending on the water demand and pump size, multiple panels are often connected in series or parallel to achieve the desired voltage and current levels. High-efficiency panels ensure better system output and reduced installation footprint.
2. MPPT Controller: Optimizing Power Generation
The Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) controller is vital for system efficiency. It constantly adjusts the voltage and current from the solar panels to ensure that they operate at their maximum power point. This dynamic optimization can boost energy harvest by up to 30% compared to non-MPPT systems. In solar pump systems, efficient MPPT control directly translates to more water delivered with the same amount of sunlight, making it indispensable for regions with fluctuating weather conditions.
3. Solar Pump Inverter: The Intelligent Power Manager
At the heart of the system lies the solar pump inverter. It converts the DC power from the panels into alternating current (AC), which is required by most commercial water pumps. Advanced inverters also manage motor speed based on the available solar power, ensuring consistent water output without damaging the pump. Some modern inverters, like those designed with hybrid input capabilities, can even accept AC power from the grid or generators to maintain pump operation during low-sunlight periods.
4. Water Pump: The Final Delivery
The water pump is the end device that moves water from the source to where it’s needed—whether it’s agricultural fields, storage tanks, or drinking water systems. Pumps may vary from submersible (for deep wells) to surface pumps (for lakes, rivers, or shallow wells). Choosing the right pump type and size is crucial for ensuring the system operates efficiently and meets daily water requirements without overloading the inverter or solar array.

How Does a Solar Pump Inverter Work?
Understanding how a solar pump inverter works helps clarify why it’s such a valuable technology for off-grid and hybrid energy applications. The system’s operation is built on the seamless coordination between solar energy capture, electrical conversion, and pump control.
Step 1: Solar Energy Collection
Everything starts with the solar panels. Installed on rooftops, ground-mounted frames, or steel poles, these panels capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity. The stronger the sunlight, the more power is generated—but even under low-light conditions, a well-configured system can still operate effectively, especially with efficient MPPT tracking.
Step 2: Voltage Optimization via MPPT
The MPPT controller continuously monitors the panel output to ensure it operates at the point of maximum power delivery. This is especially important because sunlight intensity and angle change throughout the day. MPPT ensures consistent and optimized voltage delivery to the inverter, helping the pump run smoothly without abrupt speed drops or stalls.
Step 3: DC-to-AC Conversion and Motor Control
The solar pump inverter then converts the incoming DC electricity into AC power, suitable for running standard induction or permanent magnet motors. More than just conversion, the inverter dynamically controls the motor speed in real-time, adjusting to the available solar energy. This intelligent power management prevents motor damage, reduces water hammer effects, and improves energy utilization.
Step 4: Hybrid Power Input (When Needed)
In systems with hybrid functionality, the inverter automatically switches to grid power or generator input if solar power is insufficient—such as during the night or in extended cloudy periods. This ensures uninterrupted 24/7 water supply, a critical benefit for livestock watering, drinking water systems, or sensitive crop irrigation.
Step 5: Water Delivery
Finally, the inverter supplies stable AC power to the pump, drawing water from the source and delivering it to storage tanks, irrigation lines, or distribution systems. Whether the pump is submersible or surface-mounted, the inverter ensures smooth operation with minimal manual intervention.
Where Can Solar Pump Inverters Be Used?
One of the greatest advantages of a solar pump inverter is its flexibility across a wide range of applications. Whether it’s bringing water to crops in arid regions or supplying clean drinking water in remote villages, these systems offer a sustainable and cost-effective solution.
Agricultural Irrigation
In farming, reliable water access is everything. Solar pump inverters provide an excellent alternative to diesel or grid-powered pumps, which are often expensive or unavailable in rural areas. Farmers can use these systems to irrigate crops using drip, sprinkler, or surface flooding methods—all powered directly by sunlight. By reducing fuel dependency, operating costs drop significantly, enabling long-term sustainability.
Livestock Watering and Rural Supply
Remote livestock operations often struggle with water supply, especially during dry seasons. Solar pump systems ensure that animals have continuous access to clean water without relying on fuel deliveries or unstable power lines. For rural households or communities, solar-powered pumps offer a safe, low-maintenance option for drawing water from deep wells or rivers.
Greenhouses and Controlled Agriculture
Maintaining humidity and temperature in greenhouses often requires precise irrigation and misting systems. A solar pump inverter enables automated water circulation, allowing growers to maintain stable environments without high energy costs. The ability to scale systems up or down makes them ideal for both small family farms and commercial greenhouse operations.
Off-Grid and Emergency Water Access
In disaster-prone or conflict-affected areas, reliable energy infrastructure may be non-existent. Solar pump inverters are ideal for emergency response, enabling rapid deployment of water access without reliance on fuel logistics. Similarly, in refugee camps or humanitarian missions, these systems provide safe water supply using minimal resources.
Environmental and Water Treatment Projects
From wetland restoration to wastewater filtration, solar-powered pump systems are also finding roles in environmental engineering. They can circulate water in artificial ponds, drive filtration systems, or power remote desalination units—without adding to carbon emissions or operational budgets.
Why Choose a Solar Pump Inverter?
With the increasing urgency to reduce carbon emissions, lower energy costs, and bring infrastructure to off-grid areas, the solar pump inverter has emerged as a smart, sustainable solution. Its combination of clean energy use, cost savings, and operational reliability makes it an ideal choice for a wide variety of users—from farmers and environmental engineers to humanitarian workers and rural developers.
Clean and Renewable Energy
One of the main advantages of a solar pump inverter is its reliance on renewable solar energy. Unlike diesel-powered systems, which emit harmful gases and depend on costly fuel logistics, solar-powered pumping systems run silently and cleanly. This makes them not only environmentally friendly, but also ideal for use in ecologically sensitive areas such as protected wetlands, conservation zones, and organic farms.
High Energy Efficiency with MPPT
Modern inverters are equipped with MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) technology, which ensures optimal energy conversion from solar panels to electrical output. This allows the system to perform efficiently even during partial shading, cloudy weather, or low-light conditions—maximizing water output throughout the day without needing oversized solar arrays.
Hybrid Compatibility and 24/7 Operation
Some advanced inverters support hybrid power input, which means they can automatically switch between solar power and AC sources (like generators or the grid). This provides uninterrupted operation regardless of sunlight conditions—a crucial feature for livestock, critical irrigation, and community water supply systems.
Cost Savings Over Time
Although the upfront investment in solar equipment may be higher than traditional pumps, the long-term operational costs are significantly lower. There are no recurring fuel costs, minimal maintenance needs, and a longer system lifespan thanks to fewer moving parts. Over time, the savings more than compensate for the initial setup.
Scalability and Modular Design
Whether you need to run a single small pump or a multi-pump irrigation system, solar pump inverters are highly scalable. Systems can be expanded as water demands grow, simply by adding more panels or increasing pump capacity. Their plug-and-play nature also simplifies installation and future upgrades.
Conclusion: Reliable, Sustainable Water Solutions for the Future
As global water demands increase and traditional energy systems face mounting pressure, the solar pump inverter stands out as a smart, forward-thinking solution. By harnessing solar energy, it empowers farmers, communities, and engineers to build water systems that are reliable, efficient, and environmentally sound.
Whether you’re addressing water scarcity in rural regions, reducing operating costs in agriculture, or enhancing the sustainability of infrastructure projects, a solar pump inverter can play a central role. Its intelligent design, adaptability, and energy-saving potential make it a cornerstone technology in the push toward cleaner, greener development.
If you’re planning to upgrade your existing pumping system or build a new solar water project from the ground up, choosing the right inverter is critical to success.
About LCGK
LCGK specializes in the development of high-efficiency solar pump inverters designed for real-world challenges. Featuring advanced MPPT algorithms (up to 99% efficiency), hybrid AC/DC input, motor compatibility (supporting both asynchronous and permanent magnet BLDC motors), and waterproof protection, LCGK inverters are built for durability and ease of use. Their plug-and-play installation and optional IoT remote monitoring make them ideal for applications in agriculture, livestock management, rural water access, and environmental projects.
With LCGK, you’re not just choosing an inverter—you’re investing in a reliable, future-ready water solution that works anywhere the sun shines.

❓Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What does a solar pump inverter do?
A solar pump inverter converts direct current (DC) from solar panels into alternating current (AC) to power water pumps. It also manages motor speed and system performance based on available solar energy.
Can a solar pump inverter work at night or on cloudy days?
Yes. If the inverter supports hybrid input, it can switch to grid power or generator input during low sunlight conditions, ensuring continuous operation 24/7.
What type of motors are compatible with solar pump inverters?
Most solar pump inverters support both asynchronous motors and permanent magnet BLDC motors, offering flexibility in pump selection and improved system efficiency.
Are solar pump inverters hard to install?
No. Many inverters—especially plug-and-play models—are designed for quick and easy installation without complex pre-configuration. They often come with auto-start and protection features.
Is it worth investing in a solar pump system?
Absolutely. While initial costs may be higher, long-term benefits include zero fuel costs, low maintenance, and clean, renewable energy, making it a smart investment for sustainable water access.






